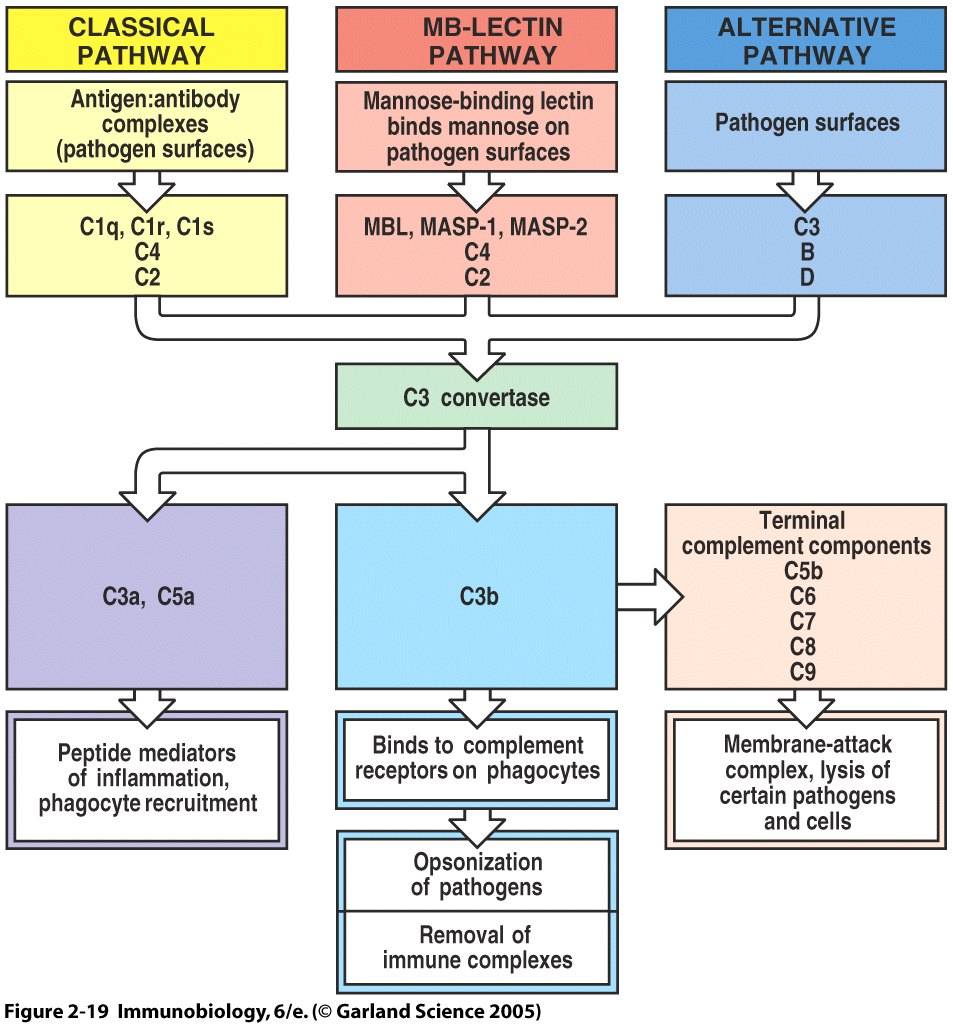
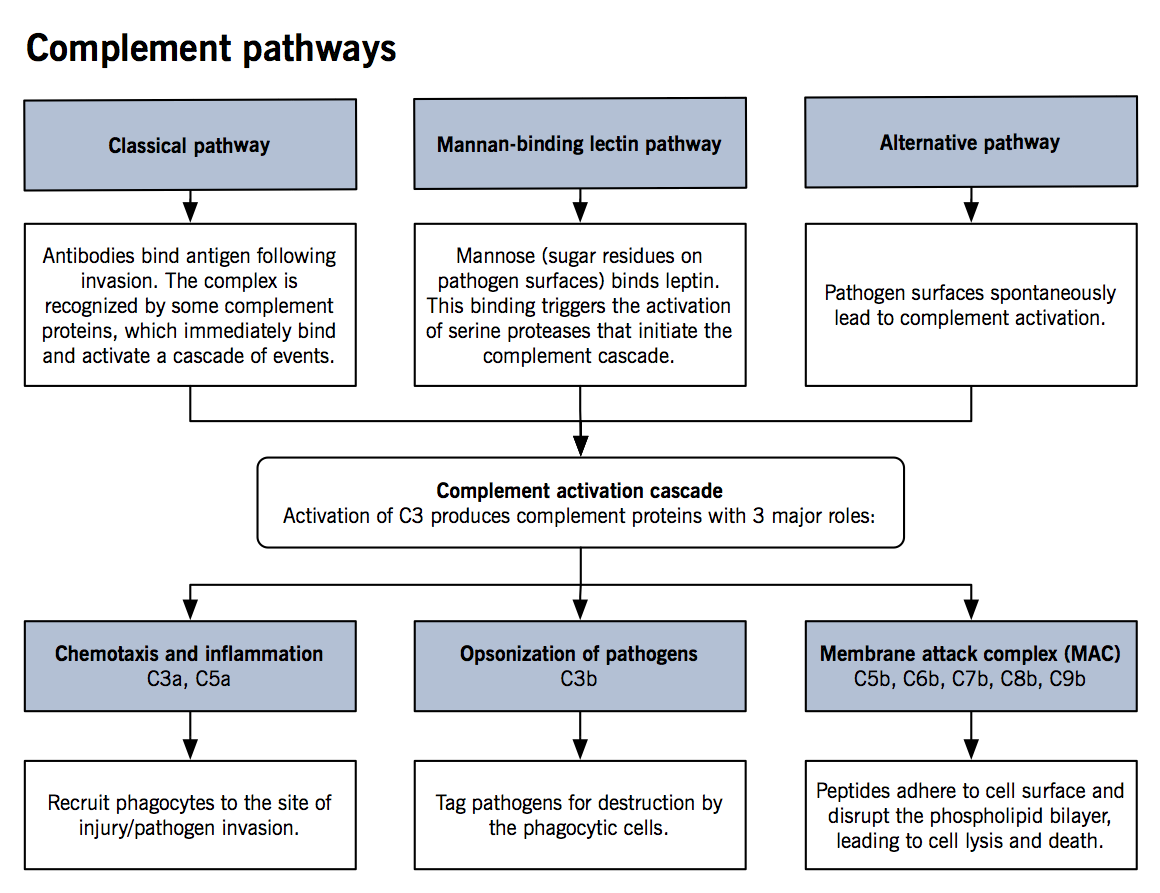
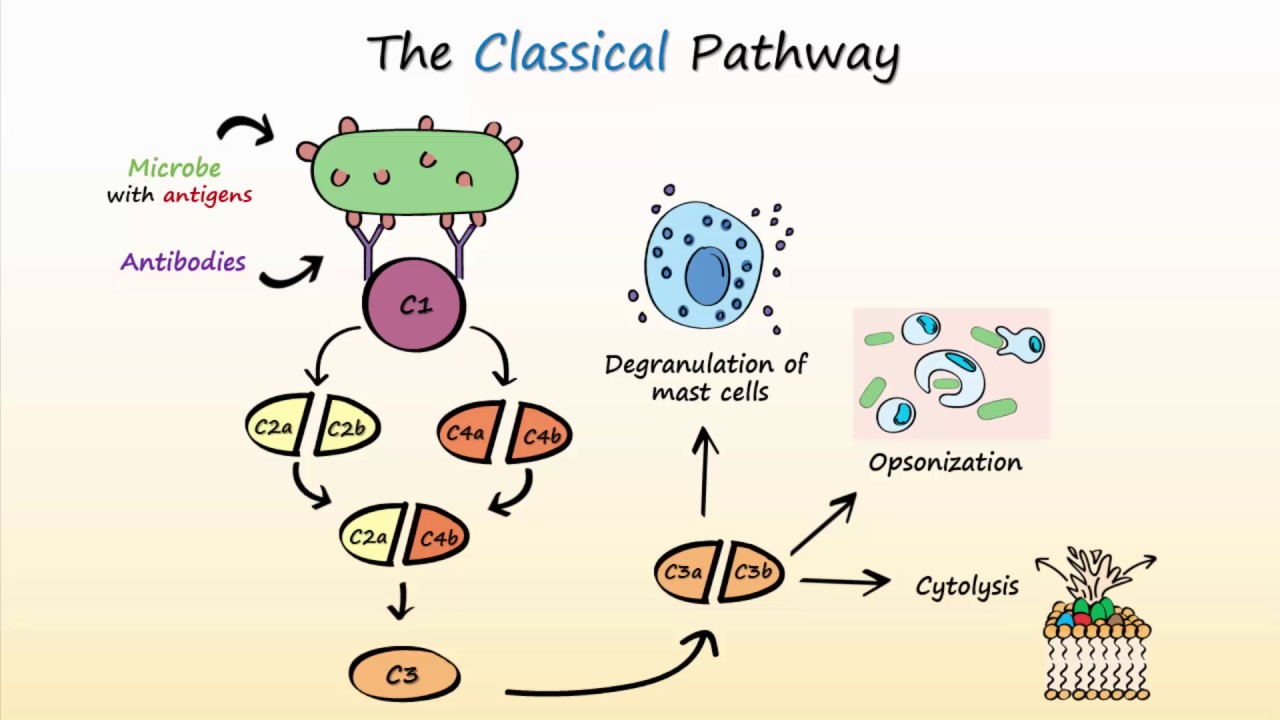
classical pathway The classical pathway is triggered primarily by immune complexes (containing antigen and IgG or IgM) in the presence of complement components 1, 4, 2, 3, Ca and Mg cations. Classical pathway: Here complement system is activated by antibodies bound to pathogen surface or antibodyantigen complexes, thus involved in specific and acquired immunity. Classical Pathway (CP) A wide variety of pathogenic microorganisms efficiently activate the CP after their recognition by antibodies. A key event for the activation is the interaction of the serum C1 complex with antibodyantigen complexes or immune aggregates containing IgG or IgM. Complement proteins recognize antibodies bound to an antigen located on an exposed surface, such as the capsule of a bacterium. Complement is activated and the bacterium is eventually lysed. Lets take a look at the classical pathway. Complement Activation Classical Pathway Clinical Significance. Because of its role in the innate immune system classical complement has been implicated in a number of pathogen related disorders. Complement is responsible for immune inflammatory response in adipose tissues which has been implicated in the development of obesity. The classical pathway requires the presence of an antibodyantigen complex. When an antibody (either IgM or IgG) locates and binds to its complementary antigen, it goes on to. circulating immune complexes become substrates for the activation of the classical pathway 2. complement fragment C3b attaches to these immune complexes, mediating attachment of the complexes to RBCs via CR1. The complement system is an enzyme cascade that helps defend against infection. Many complement proteins occur in serum as inactive enzyme precursors (zymogens); others reside on cell surfaces. The complement system bridges innate and acquired immunity by Classical pathway components are labeled with a C and a number (eg, C1, C3), based on. The Classical Complement Pathway is a component of the innate immune system. The innate immune system serves as a constant nonspecific defense against foreign pathogens including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. The classical pathway is the major effector function of the complement system in humoral immune response. Either IgG or IgM antibody bound to antigen triggers the classical pathway. Binding of antibody to antigen exposes Fc region the binding and activating site for. complement system classical pathway animation This lecture explains about the classical pathway of complement activation. This is an animation about the complement system about the classical. Typically to activate the classical complement pathway, IgG or IgM is made in response to an antigen. THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW. CELLS INVOLVED IN BODY DEFENSE 1. Defense Cells in the Blood: The Leukocytes. Alternative complement pathway. Complement system is a major effector of humoral branch of the immune system, acting to protect the host from microorganisms, such as bacteria. Alternative Pathway (AP) The Alternative pathway (AP) is one of the three pathways of the complement system. In contrast to the other two pathways the AP is not triggered by antibodies or specific structures on the microorganisms. This pathway involves complement components C1, C2 and C4. The pathway is triggered by antibodyantigen complexes binding to C1, which itself has three subcomponents C1q, C1r and C1s. The pathway forms a C3 convertase, C4b2a, which splits C3 into two fragments; the large fragment, C3b, can covalently attach to the surface of microbial pathogens and opsonise them; the. Complement system Alternative pathway kit is an enzyme immunoassay for the qualitative determination of functional alternative complement pathway in human serum, the result shall not be used for clinical diagnosis or patient management. The complement system is a welldefined series of soluble proteins, enzymes, and receptors that act as a cascade to mediate a wide range of effector functions. The mouse classical complement pathway ELISA is a qualitative semiquantitative ELISA to be used for the in vitro determination of activation of the classical pathway of. The alternative pathway of the complement system is an innate component of the immune system's natural defense against infections. The alternative pathway is one of three complement pathways that opsonize and kill pathogens. The complement system is an important antimicrobial and component of the innate immune system. The classical pathway of complement is activated upon binding of the 774kDa C1 complex, consisting of the recognition molecule C1q and the tetrameric protease complex C1r 2 s 2, to a variety of activators presenting specific molecular patterns such as IgG and IgM. Classical complement pathway Complement system is a major effector of the humoral branch of the immune system, acting to protect the host from microorganisms such as bacteria. Complement components are designated by numerals ( C1 C9 ), by letter symbols (e. , Complement factor I ( Factor I )), or by trivial names. Complement is a system of plasma proteins that interacts with pathogens to mark them for destruction by phagocytes. In the early phases of an infection, the complement cascade can be activated on the surface of a pathogen through any one, or more, of the three pathways shown in Fig. The classical pathway can be initiated by the binding of C1q, the first protein in the complement. The complement system is an ancient host defense system that traces its biologic origins to more than one billion years ago. It is part of innate and adaptive immunity, and it guards the host's intravascular space by opsonizing and lysing bacteria. Innate immune system soluble proteins called pentraxins, can also bind C1q and initiate the classical pathway. The alternative pathway, which was discovered later but is phylogenetically older than the classical pathway, is triggered when a complement protein called C3 directly recognizes certain microbial surface structures, such as bacterial LPS. C5 convertase, generated by the alternative, classical, or lectin pathway, initiates the activation of late components of the complement system to form membrane. Complement pathwayA) Classical pathway: Complement is activated by antigen antibody complex (IgM or IgG) Fc portion of the antibody form a binding site for C1q The numerical sequence of the complement factors in the classic pathway is: C1, C4, C2, C3, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9 The rat classical complement pathway ELISA is a qualitative semiquantitative ELISA to be used for the in vitro determination of activation of the classical pathway. The complement system and the natural antibody repertoire provide a critical firstline defense against infection. The binding of natural antibodies to microbial surfaces opsonizes invading microorganisms and activates complement via the classical pathway. The classical complement pathway is a component of the innate immune system. The innate immune system serves as a constant nonspecific defense against foreign pathogens including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Complement System Made Easy Immunology Classical Alternate Lectin pathway Video Sep 07, 2018 The complement system is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promotes inflammation, and attacks the pathogen's plasma membrane. In immune system: Activation of the complement system one to be discovered, the classical pathway, which is initiated by antigenantibody complexes; and the alternative pathway, which is triggered by other means, including invading pathogens or tumour cells. Recognition unit (cognitive phase) C1q, C1r, C1sActivation unit (activation) C3 convertaseMembrane Attack Complex (effector) C5C6C789 Effector phase is the formation of MAC wher the complement system makes a hole in the target and lysis the target. The Classical Complement Pathway is a component of the innate immune system. The innate immune system serves as a constant nonspecific defence against foreign pathogens including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Saunders, in The Immune Response, 2006 II. The next substrate in the classical complement pathway is the plasma glycoprotein C4. In its inactive preprotease form, C4 is a heterotrimer (210 kDa) of three polypeptides labeled, , and. The Classical pathway of activation of the complement system is a group of blood proteins that mediate the specific antibody response. [source: Wikipedia The Classical pathway begins with circulating C1Q binding to an antigen on the surface of a pathogen, which goes on to active and recruit 2 copies of each C1R and C1S, forming a C1 complex. The complement system is an enzyme cascade that helps defend against infection. Many complement proteins occur in serum as inactive enzyme precursors (zymogens); others reside on cell surfaces. The complement system bridges innate and acquired immunity. complement activation are shown. Eventually, all three pathways lead to the formation of C3 convertases (C4b2b represents the classicallectin pathway C3 convertase, and C3bBb the alternative pathway C3 convertase), which activate the central component C3. The complement system is a part of the immune system that helps or complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. complement component of the classical pathway, C1. C1 is a macromolecule that consists of C1q (comprised of 6 globular heads and extended tails) in complex with C1r and C1s (the C1qrs complex). Creactive protein is an acute phase reactant that can activate the classical pathway of the complement system, and its role in the complement led ischemiareperfusion injury (IRI) has been shown in intestinal and myocardial animal IRI models [34, 59. Classical Pathway of Complement System Duration: Alternative Pathway of Complement System Duration: The Classical Pathway of Complement Activation Duration. In this article we will discuss about the classical and alternative pathways of complement system. The Classical Pathway of Complement: The classical pathway of complement is initiated by the interaction of antibody with antigen directly (soluble antigenantibody complexes or immune complexes). The Wieslab Complement system Classical pathway is an enzyme immunoassay for the qualitative andor semiquantitative determination of functional classical complement pathway in human serum. The analysis should be performed by trained laboratory professionals. Classical Pathway Complement System Bing Videos, This is a clip that I got in class of the classical pathway of the complement system along with the terminal reaction sequence. How to create original plays for your custom playbook. the complement system provides the actual protection from the response while (reminiscent of the operation of the blood clotting system ). The Classical Pathway The early complement components are also important for solubilizing antigenantibody complexes assisting in their catabolism and elimination from the body. The complement system can be activated by three different pathways: the classical, the lectin, and the alternative pathway (Ref. The classical pathway of complement activation has always been regarded as the major effector for antibody action. The intraarticular deficiency of C1, C2, C3, C4, and CH50 in JIA revealed evidence of activation of the classical pathway (CP) of the complement system in the synovial fluid (SF). Miller found an intraarticular deficiency of C3c and C3d in JIA [ 6..